Vital Use Cases
Bio-based ThermoPlastics (b-bTPs) are not currently being adopted as a part of “circular by design” business models to replace fossil-based solutions across thermoplastic processing value chains This situation will only change when the price and processability of b-bTPs become commercially viable. Foamed polymer products are a critical part of the modern global economy, with the global foam plastics market estimated at $102.0(€87.0)Bn in 2019, predicted to increase to $123.7(€105.5)Bn by 2027.
The 7 applications presented below are only the first, immediate opportunities but there are thousands of components that can be converted to bio-based materials once the processes are successfully demonstrated in VITAL within these end users. Alongside endless opportunities with these end users, VITAL will also encourage other leading organisations in these industries to adapt and adopt.
Focussing on just the components in VITAL, approximately 75,000 tonnes CO2 eq per annum from fossil-based materials can be mitigated through the conversion to bio-based materials.

Uses Cases

ARÇELIK
Fridge EVA Cover
This component is currently made of synthetic ABS
(Starex SD-0150).
Fridge Vegetable Tray
This component is currently made of synthetic HIPS (Styrolution PS 454N).
The aim is to shift towards new materials with bio-based content to obtain an improvement of >85% ( >85% of PLA)
Arçelik will build on their Bio Refrigerator concept – BioFridge is made using bio-based polyurethane insulation material (Bio-Cool) and bio composite raw materials that contain at least 15% organic material such as soy and castor oil. In VITAL, Arçelik will look at the refrigerator liner and the vegetable tray to further the bio-based components within this product range. VITAL will aim to replace ~845.7 tonnes HIPS and ~309 GPPS per annum for these two parts which create a combined carbon impact of ~3015 tonnes CO2 eq per annum from the material consumed for production. These parts will be replaced with bio-based alternatives such as PLA

Demostrator and Tear1: FARPLAS
OEM: TOFAS / STELLANTIS
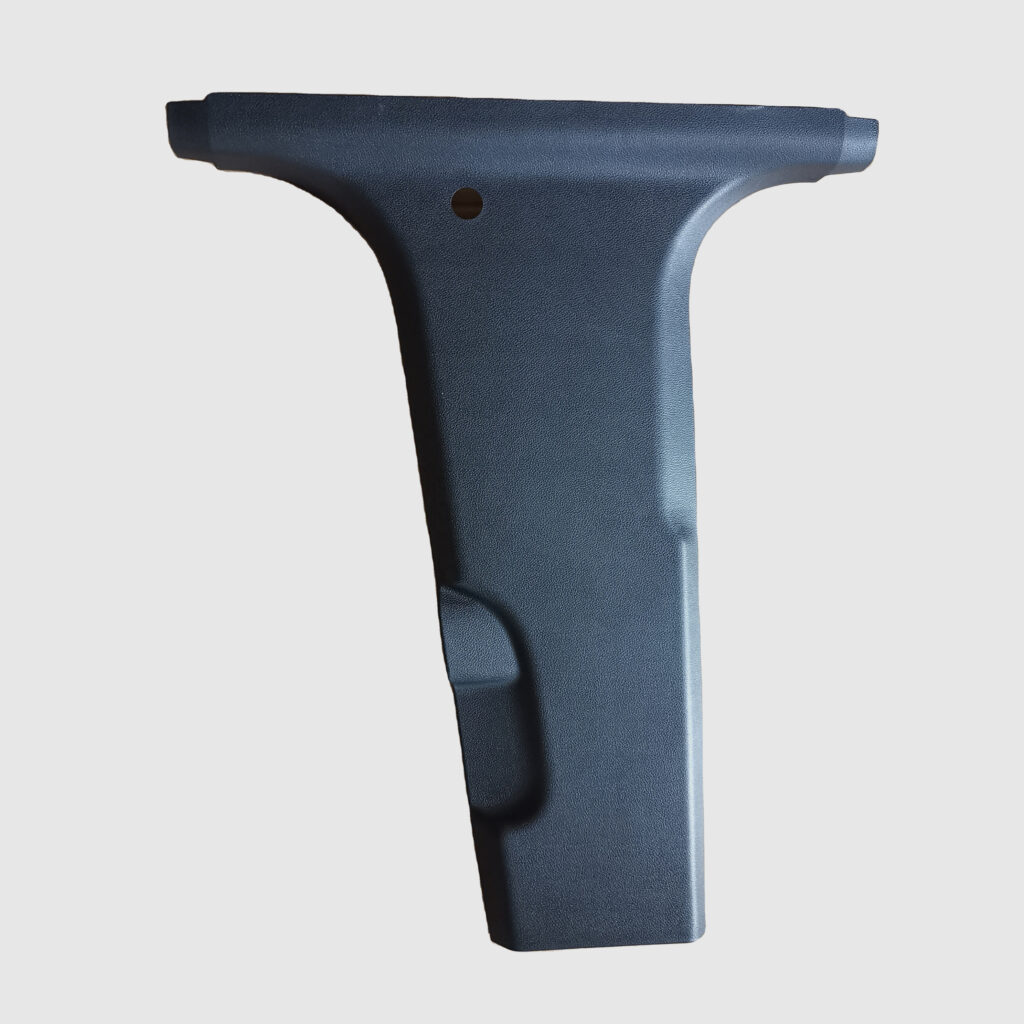
Doblo B Pillar Lower
This component is currently made of synthetic PP Poypropylene with talc filled materials.
Tipo B Pillar Lower
This component is currently made of synthetic PP (HOSTACOM CR1171G).
Farplas / Tofaş will demonstrate production for high-volume automotive interior trim parts (B-Pillar Lower) for top selling vehicles – Fiat Doblo and Fiat Tipo (Egea in Turkey). Tofaş produced >250k vehicles in 2020 (down from 264K in 2019 due to COVID market and production pressures); of which 151.7k Egea/Tipo models were produced and 68.8k Doblo models. The B-Pillar lower is required in double for every vehicle, creating a high-volume opportunity for up to 440k components per year, before rolling out to further production models in the Tofas range.

Stellantis (CRF)
Automotive Seat Foams
This component is currently made of PU-foam.
Front Dust Cover
This component is currently made of rigid TPU.
CRF (representing Stellantis) manufactures many limited-edition, limited-volume vehicles, with high-degrees of customisation. With CRF, VITAL will demonstrate the ability to make automotive seating using both bead foaming and 3D foam printing. This application will look to replace traditional 2K Polyurethanes with a b-bTP alternative. Annually, for seating applications CRF/Stellantis consumes ~20,000 tonnes of PU foams which creates a carbon impact of ~71,200 tonnes CO2 eq per annum. With VITAL demonstrating bio-based alternatives this 20,000 tonnes can be replaced along with the other ~15,750 tonnes used for other PU interior automotive applications (each car uses ~15kg of PU foams).

MEYER
Ship Interior Facades
Meyer Shipyards are demonstrating 3D printed B-bTP panels. Enabling cost effective unique elements in use-cases with limited production volumes with no need for mould production. These cases are quite common in cruise-ships, which need to have interesting interior, but only produced in single digits.
The main considerations are mechanical and fire retardant performance for interior or exterior visual facades and panels. Where applicable aesthetic, non-structural fibreglass, gypsum or MDF constructions could be replaced with sustainable bio-based thermoplastics, using 3D printing.